
View of the tower from the courtyard
The tower is located at the heart of Haghill and the curtain wall facade offers the opportunity to empower, encourage and promote activities through signage on the windows. The central space can also be used to sit, meet, socialize and spend time in the day.
View of the tower from the courtyard

Centre for Sisterhood Approach
The tower is the control centre for safety around the city and represents Jane Jacobs’ conceptual theories for ‘eyes on the street’. Visually, it is a metaphor for representing safety in architecture by adopting elements of watchtowers and lighthouses.
Centre for Sisterhood Approach
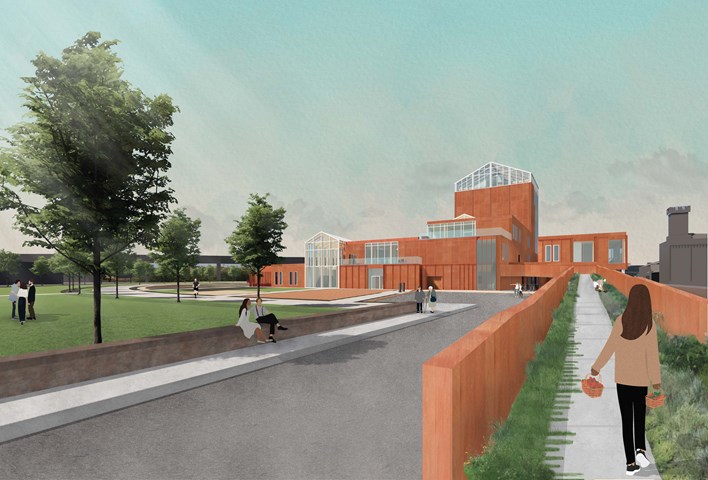

The Ramp Entrance - public access directly to the market, restaurant, garden spaces, and new public park
The site rests on a plinth that is 3.5m above the main street level, and has an existing ramped entrance. To continue the pedestrian walkway in Tradeston's proposed new masterplan, people can directly access the market and gardens without having to go through the whole building. To promote more exterior access, as the site ramps up, so does the building, with a nature path. The nature path wraps around the building, providing direct access from that side of the building to the restaurant, the market seating, the growing areas, and the main greenhouse, all while continuing a green journey to experience the building and create views over the historical wall to the rest of Glasgow.
The Ramp Entrance - public access directly to the market, restaurant, garden spaces, and new public park
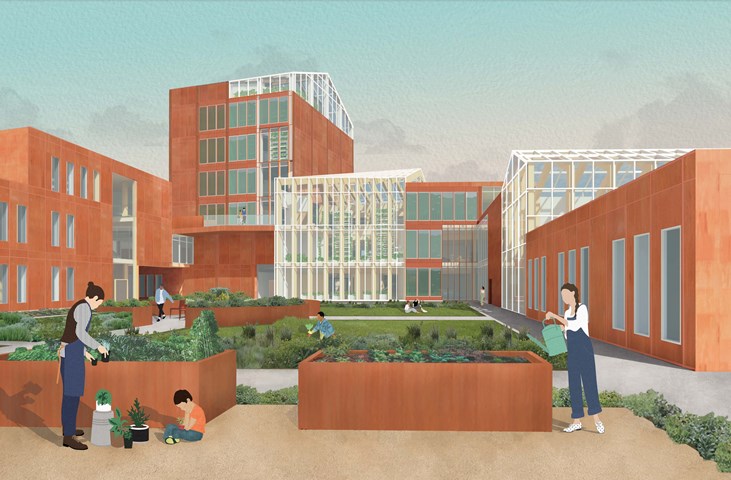

The Garden Approach
The exterior view of the south side of the building, among the community gardening plots and the courtyard. Alongside the greenhouses, a secondary facade of algae growing panels are on the south side of the building to help generate renewable energy in the form of biomass, which then feeds back into an anaerobic digestor to create energy for the building.
The Garden Approach
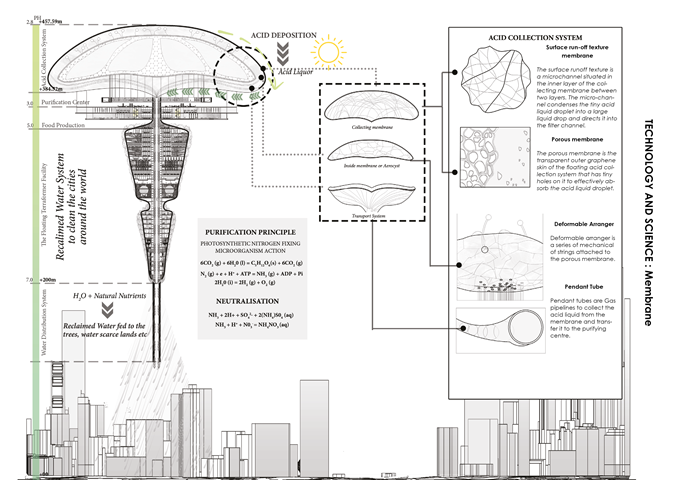
The brain of the Facility: Membrane
the brain of the facility: the membrane. It’s divided into three parts. The outer membrane or the collecting membrane, the inner membrane, and the transport system. The collecting membrane is further divided into two parts, the surface run-off texture which is a microchannel situated in the inner layer of the collecting membrane that condenses the tiny acid liquid droplets and directs them to the filter channel. And the porous membrane, which has a transparent outer graphene skin with tiny holes on it that effectively absorb the big acid droplets coming from the filter channel.
Last but not the least the transport system consists of pendant tubes that acts as gas pipelines to collect the acid liquid from the membrane and transfer it to the purification center.
Inspiration of the project taken from: PH Conditioner skyscapper, Evolo, 2012
The brain of the Facility: Membrane
Inspiration of the project taken from: PH Conditioner skyscapper, Evolo, 2012

Example of a 'safe wing'- Laundrette
The laundrette is the most important medium sized intervention in this context as it is promotes an easy and independent activity that is also familiar to an elderly person. Informal encounters/ conversations can have a positive impact on an elderly persons daily life. The chosen coral/ yellow tones encourage social activity and invite the elderly to spend a longer times with their neighbours and other locals.
Example of a 'safe wing'- Laundrette